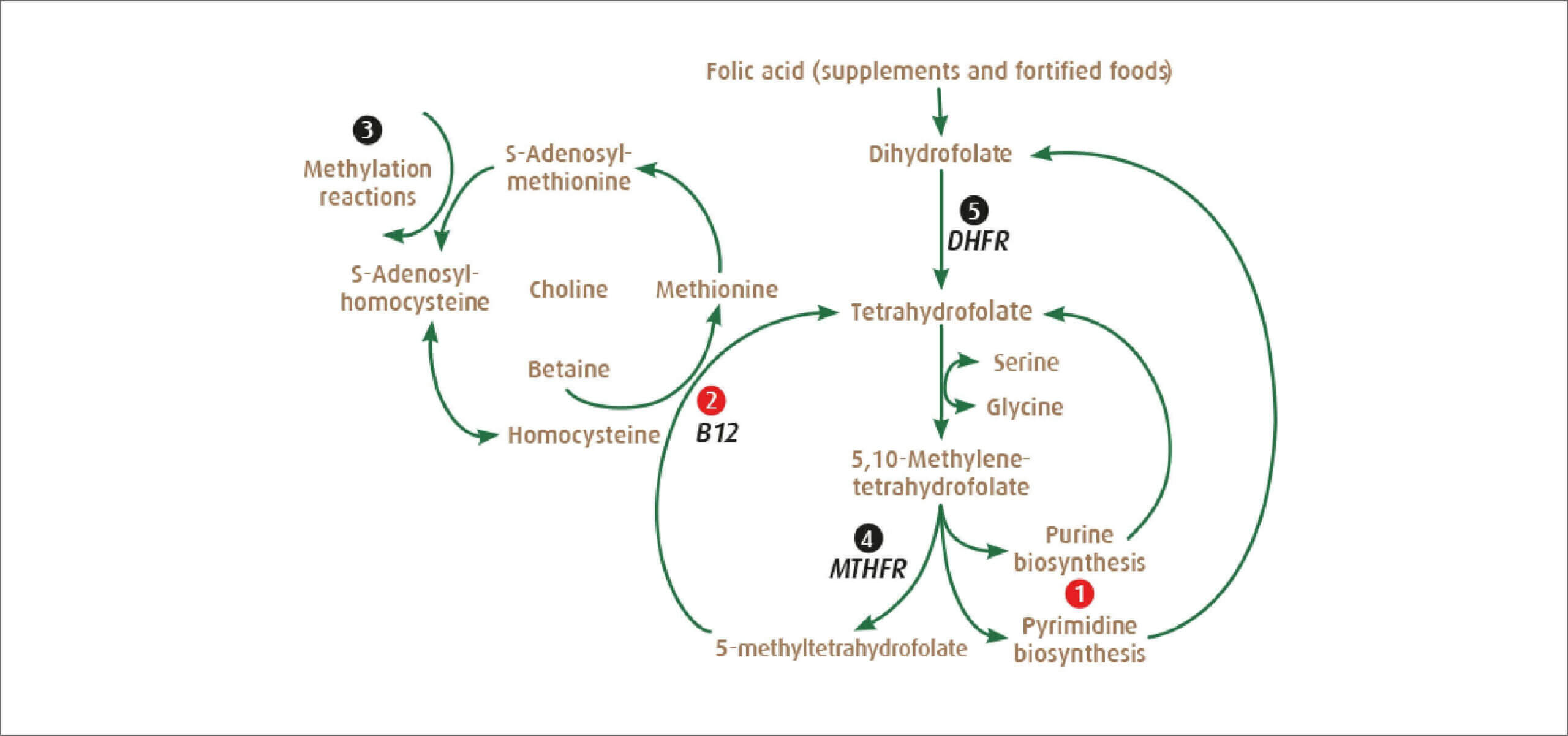
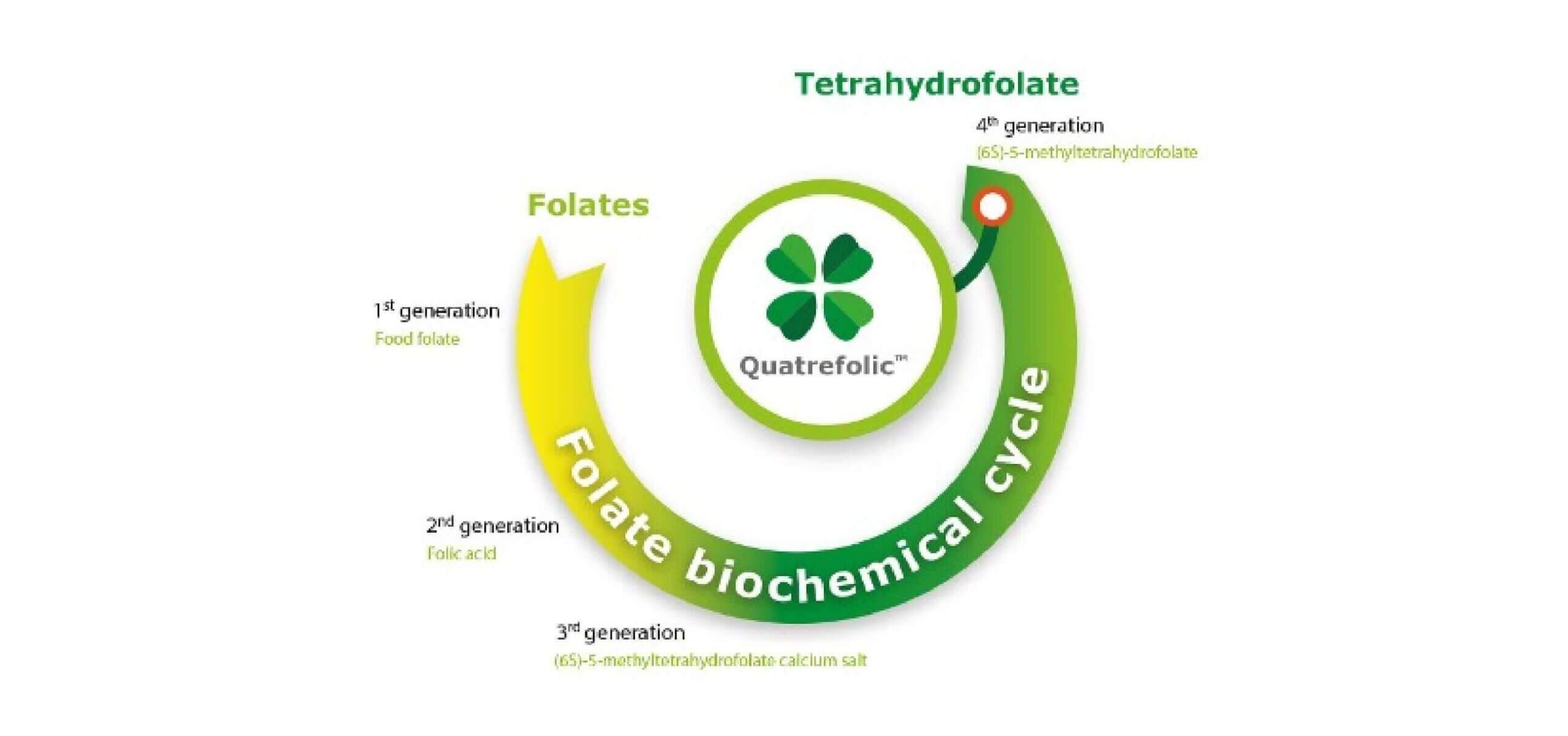
The mechanism of action of Quatrefolic® is related to the action of 5-methyltetrahydrofolate the active part of the proprietary ingredient. 5-methyltetrahydrofolate derives from tetrahydrofolic acid, through a series of metabolic reactions. Tetrahydrofolic acid acts as a coenzyme in several vital metabolic reactions participating in the transfer as acceptors and donors of various one-carbon fragments, involved in the biosynthesis of nucleotides purines and pyrimidines, and in the metabolism of several important amino acids.
In concert with vitamin B12, folate coenzymes allow the conversion of the amino acid homocysteine into methionine. The lack of this conversion has been associated with various pathologies and diseases. Conversion of tetrahydrofolic acid into 5-methyltetrahydrofolate is mediated by the action of the enzyme methylentetrahydrofolate reductase. In individuals with a genetic defect of the methylentetrahydrofolate reductase (MTHFR) this enzyme conversion is limited, consequently it will predispose these individuals to an increased risk for certain disease conditions.
Supplementation with 5-methyltetrahydrofolate is preferable to the one with folic acid, à immediately bioavailable to react with homocysteine to avoid the possibility to incur in hyperhomocysteinemia.