What is folate
What is folate
Folate is the natural form of vitamin B9; a water-soluble vitamin that is naturally found in many foods, including dark green leafy vegetables, nuts and legumes.
In order to produce DNA – which we need to grow and repair every cell in our body – we need folate. In fact, folate plays a direct role in the production all DNA in our body.
Folate is also needed in the formation of red blood cells and is vital for cells in our body to grow and divide. Because of this, folate is crucial for fertility and during early pregnancy, where it has been shown to reduce the risk of birth defects.
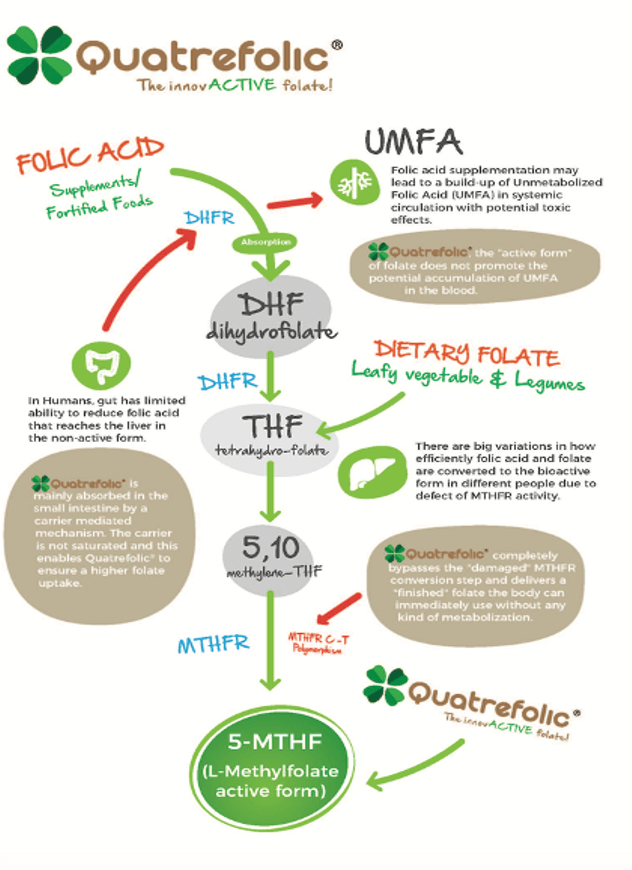
However, like many essential nutrients, humans cannot produce folate, meaning we must get it from our diet. It is also added to foods and sold as a supplement – often in the form of folic acid, which is a synthetic form of the vitamin that is the inactive precursor to biologically active folate.
Many governments and health authorities recommend folate or folic acid supplementation. Both the European Food Safety Authority (EFSA) and the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) have set recommendations for folate intake to maintain health at every stage of life.
EFSA has set a dietary reference value (DRV) for folate in healthy adults at 330 micrograms per day and a DRV for pregnancy and lactation at 600 micrograms and 500 micrograms per day, respectively. Meanwhile, the FDA has a Daily Value (DV) of 400 micrograms per day for healthy adults and recommends that women who are pregnant should consume 600 micrograms daily, while those who are breastfeeding should consume 500 micrograms per day.
Some governments also mandate the fortification of foods with folic acid to help ensure people are not deficient.