What is new in science about Quatrefolic® and fertility problems?


Assisted Reproductive Technologies (ART) represent widely used procedures for the control and treatment of infertility, despite that the majority of procedures remain unsuccessful, and the reason for this lack of success may have a multifactorial origin. Reproductive success is highly influenced by the female pre-conceptional health, including nutrition and micronutrient levels, which may play a pivotal role in this initial phase.
A very interesting investigation target is today represented by Folate and vitamin B12. The shortage of these vitamins results in increased serum homocysteine (hyperhomocysteinemia, Hcy) which is believed to have important embryotoxic effects and adverse obstetric/neonatal outcomes.
High homocysteine has a role in the increase of spontaneous pregnancy loss, and a defect in vascularization of the chorionic villi. Furthermore, the levels of homocysteine in the follicular fluid seem to be inversely related to oocyte maturity and embryo developmental capabilities in vitro.
Therefore, testing for homocysteine, vitamin B status, as well as MTHFR polymorphisms in the preconception period, should be useful in highlighting micronutrients deficiencies and warrant an optimal multivitamin supplementation before ART as preconception care.
Accordingly to the new study just published by Cirillo et al. (Cirillo M et al. 5-Methyltetrahydrofolate and Vitamin B12 Supplementation Is Associated with Clinical Pregnancy and Live Birth in Women Undergoing Assisted Reproductive Technology. Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2021), women undergoing ART supplemented with vitamin B complex (5-methyltetrahydrofolate as Quatrefolic® plus vitamins B12 and B6 – Normocis®commercialized by the Italian company Inpha Duemila Srl) -have a higher chance of clinical pregnancy and live birth in comparison with those with only folic acid, and that supplementation might be considered in clinical practice, especially in those women undergoing ART.
269 infertile women participated in this study: a group A (111 women) were supplemented daily with Quatrefolic®associated with other vitamin B and the group B (158 women) with only FA.
In the vitamin B complex-supplemented subjects, the mean number of Metaphase II oocytes and the pronuclear stage (2PN) fertilization rate score were higher than in women supplemented with FA. A higher percentage of women in the vitamin B complex group had a clinical pregnancy and live birth in comparison to the FA group.
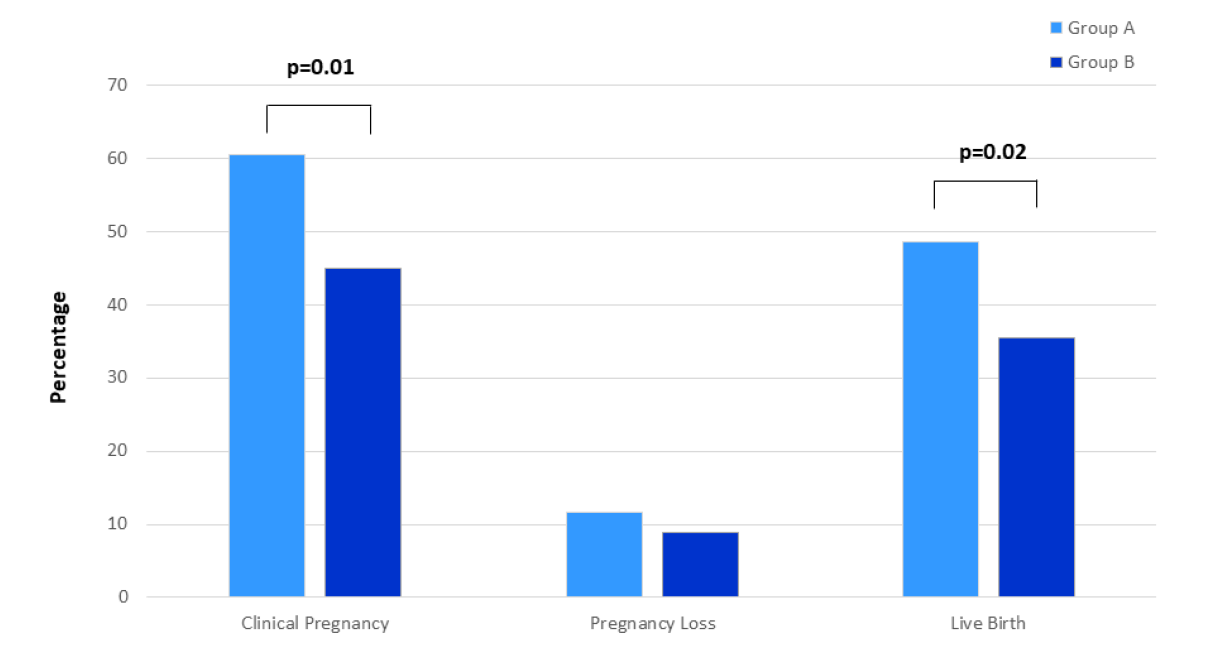
Figure 1: Distribution of pregnancy ART outcomes (percentage of clinical pregnancy, pregnancy loss and live birth) in women undergoing Assisted Reproduction supplemented with vitamin B complex (Group A) and folic acid (Group B).
“Quatrefolic® is proven to be a real solution for fertility, with beneficial innovated features that match totally to the requirements of physicians and doctors to provide effective solutions and increase consumers’ compliance” – says Silvia Pisoni Global Market Manager of Reproduction and Women’s Health.
She added: “This study strengthens the positioning of Quatrefolic® in fertility, already shown by observational studies conducted on couples with a history fertility problem such as recurrent fetal loss, premature ovarian insufficiency, or abnormal sperm parameters (2,3,4,5)
1. Cirillo, M.; Fucci, R.; Rubini, S.; Coccia, M.E.; Fatini, C.5-Methyltetrahydrofolate and Vitamin B12 Supplementation Is Associated with Clinical Pregnancy and Live Birth in Women Undergoing Assisted Reproductive Technology. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2021, 18, 12280. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph182312280.
2. MTHFR isoform carriers. 5-MTHF (5-methyl tetrahydrofolate) vs folic acid: a key to pregnancy outcome: a case series – PubMed (nih.gov) Servy EJ et al. J Assist Reprod Genet 2018; 35:1431–5.
3. The Methylene Tetrahydrofolate Reductase (MTHFR) isoform challenge. High doses of folic acid are not a suitable option compared to 5 Methyltetrahydrofolate treatment (oatext.com) Servy EJ, Ménézo Y. Clin Obstet Gynecol Reprod Med 2017; 3.
4. 5-Methyltetrahydrofolate reduces blood homocysteine level significantly in C677T methyltetrahydrofolate reductase single-nucleotide polymorphism carriers consulting for infertility – PubMed (nih.gov) Clément A et al. J Gynecol Obstet Hum Reprod 2020; 49:101622.
5. MTHFR (methylenetetrahydrofolate reductase: EC 1.5.1.20) SNPs (single-nucleotide polymorphisms) and homocysteine in patients referred for investigation of fertility | SpringerLink Ménézo Y et al. Y. J Assist Reprod Genet 2021.