New study shows significant effect of Quatrefolic® in lowering Homocysteine Serum Levels
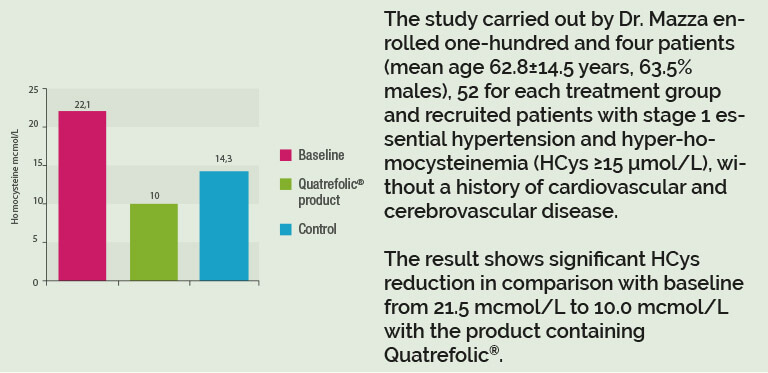

The treatment was significantly effective and the ideal HCys level was reached in 55.8% of cases in the Quatrefolic® group, and it was significantly higher than in controls.
No side effects were observed in either treatment group. Homocysteinemia is widely accepted as an independent risk factor for coronary, cerebral, and peripheral vascular diseases.
Homocysteine is a metabolite of methionine metabolism in the one-carbon metabolism, often referred to as the methylation cycle, and exists at a critical biochemical intersection – between S-adenosylmethionine, the indispensable ubiquitous methyl donor, and 5-MTHF and vitamins B12[1].
Homocysteinemia may be caused by several nutritional deficiencies other than B12, including vitamin B6 and folate deficiencies[2], and decreasing plasma total homocysteine by providing nutritional cofactors for its metabolism has been shown to reduce the risk of cardiovascular events.
High blood levels of homocysteine signal a breakdown in this vital process, resulting in far-reaching biochemical and life consequences. As a matter of fact, the link between homocysteine and cardiovascular disease is well established especially in the elderly[3]. High Hcys concentrations inhibit the proliferation of vascular endothelial cells[4], decrease the antioxidant activity of superoxide dismutase on endothelial cell surfaces, and impair endothelial function[5] They are also implicated in the pathophysiology of essential hypertension[6]. Hyperhomocysteinemia exerts its deleterious vascular effects through the production of free-reactive oxygen species that cause oxidative stress[7] as a result of antioxidant/prooxidant imbalance and probably also by inhibition of intracellular glutathione peroxidase[8,9].
References: